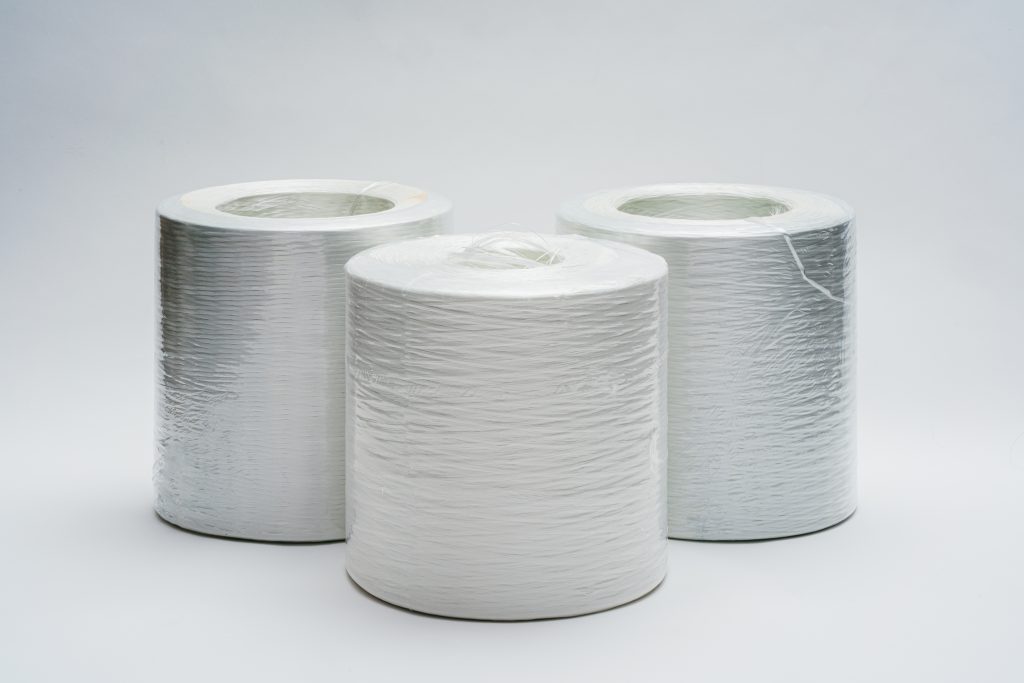
What is Direct Roving?
Direct roving is a crucial reinforcement material used widely in the composites industry, especially in applications requiring strength, durability, and lightweight performance. It serves as a base material for products like fiberglass-reinforced plastics (FRP), pipes, pressure vessels, wind turbine blades, and automotive parts.
It is a bundle of continuous glass filaments that are drawn directly from the bushing and wound into a package without further processing. This differentiates it from assembled roving, which is created by twisting or assembling strands from multiple packages.
Each filament in direct roving is typically coated with a size (or sizing agent) that enhances compatibility with specific resins (like polyester, epoxy, or vinyl ester) and improves processing efficiency.
What is composition of the glass?
There are multiple compositions of general glass products. Main composition of fiberglass is generally E glass (“Electric Glass”). E glass contains around 53-56% SiO2. Its strength is heat and insulation resistance. The softening point of E-glass is around 850℃. The heat-resistance temperature of glass roving is said to be around 160℃.
| E glass | C glass | S glass | D glass | |
| SiO2 | 55 | 65 | 65 | 70 |
| Al2O3 | 10-15 | 5 | 25 | 1 |
| CaO | 20 | 15 | – | 1 |
| MgO | ~2 | ~3 | 10 | – |
Key Characteristics
- Tex and Filament Count: Direct roving comes in different weights, called tex. With popular options like 1200 tex, 2400 tex, 4800 tex, etc.
- 1200 tex means the yarn weighs 1,200 grams per kilometer.
- 2400 tex and 4800 tex are thicker and heavier options.
- The right size depends on what the customer needs — thinner for fabrics, thicker for big products like tanks.
- Even Tension: Since it comes from a single package, direct roving offers consistent tension, which improves processing quality.
- Good Dispersion: The filaments are well-separated, helping with even wet-out and minimal fuzz.
- Tailored Sizing: Manufacturers can adjust the sizing to improve bonding with various resins and matrices.
Advantages of Direct Roving
- Higher Strength: Continuous and uniform fibers enhance mechanical properties.
- Excellent Processability: Especially in applications like pultrusion, filament winding, and weaving.
- Reduced Fuzz: Minimizes equipment wear and enhances surface quality.
- Cost-Effective: Offers better performance per unit cost compared to assembled rovings in many cases.
Applications
- Filament Winding: For pressure vessels, chemical storage tanks, and pipes.
- Pultrusion: Used to create structural profiles like beams, gratings, and rebar.
- Weaving and Knitting: For producing woven or stitched fabrics for composite laminates.
- Chopped Strand Production: Can be chopped into various lengths for compounding and reinforcement in thermoplastics.
Packaging and Handling
Direct roving is usually supplied in 5–20 kg rolls and packed on pallets, with care taken to avoid moisture and physical damage. Rolls are often shrink-wrapped and stacked in standard configurations (e.g., 24 rolls per pallet), depending on TEX and customer specifications.
Conclusion
Direct roving is a foundational material in composite manufacturing, known for its strength, uniformity, and versatility. As industries increasingly turn toward lightweight, high-strength materials, direct roving continues to play a vital role in shaping products that are both strong and efficient. Choosing the right type of roving — with proper TEX, sizing, and compatibility — can significantly impact both production efficiency and final product performance.
Feel free to contact us about Direct Roving in Thailand!